

Lifeline Hospital’s Department of Radiology provide diagnosing and treating injuries and diseases using medical imaging (radiology) procedures (exams/tests) such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) and ultrasound.
Radiology plays several crucial roles in medicine. It can be used for advanced testing and treatment, for screening and wellness, and to detect diseases and conditions. Think of radiology as a huge umbrella, with many specific technologies underneath it.
In the realm of testing and treatment, there is a wide range of radiology techniques, including, but not limited to:
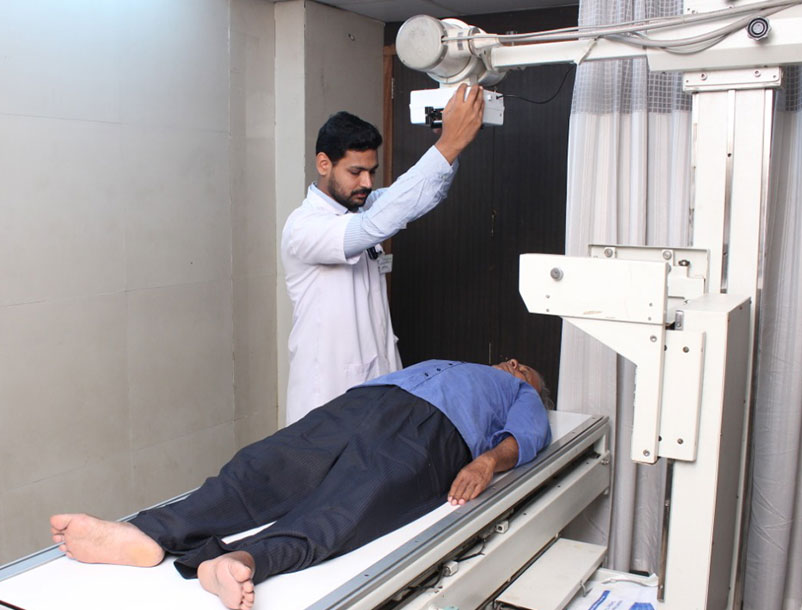 X-ray, or radiography, is used to diagnose fractured bones, detect injury or infection, or to locate foreign objects in soft tissue. Some x-ray exams employ an iodine-based contrast material to clarify the visibility of specific organs like the heart, lungs, blood vessels or tissues.
X-ray, or radiography, is used to diagnose fractured bones, detect injury or infection, or to locate foreign objects in soft tissue. Some x-ray exams employ an iodine-based contrast material to clarify the visibility of specific organs like the heart, lungs, blood vessels or tissues.
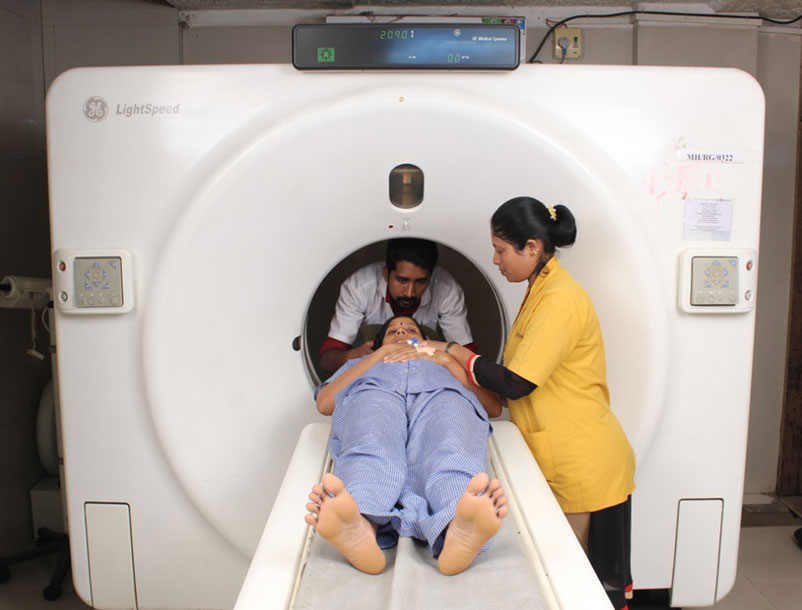
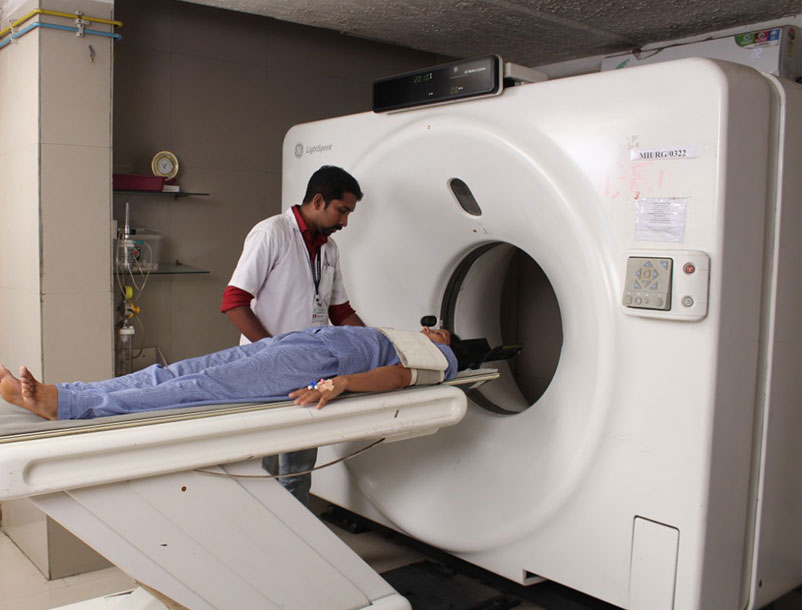 Computed tomography (CT) creates detailed images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels. CT is considered by many doctors as the preferred method to detect cancer, since it can confirm the presence of a tumor and determine its size and location. In emergency cases, CT can quickly reveal internal injuries and bleeding to help save lives.
Computed tomography (CT) creates detailed images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels. CT is considered by many doctors as the preferred method to detect cancer, since it can confirm the presence of a tumor and determine its size and location. In emergency cases, CT can quickly reveal internal injuries and bleeding to help save lives.
 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to detect conditions such as tumors and diseases of the liver, heart and bowel. MRI may also be used to monitor an unborn child in the womb.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to detect conditions such as tumors and diseases of the liver, heart and bowel. MRI may also be used to monitor an unborn child in the womb.
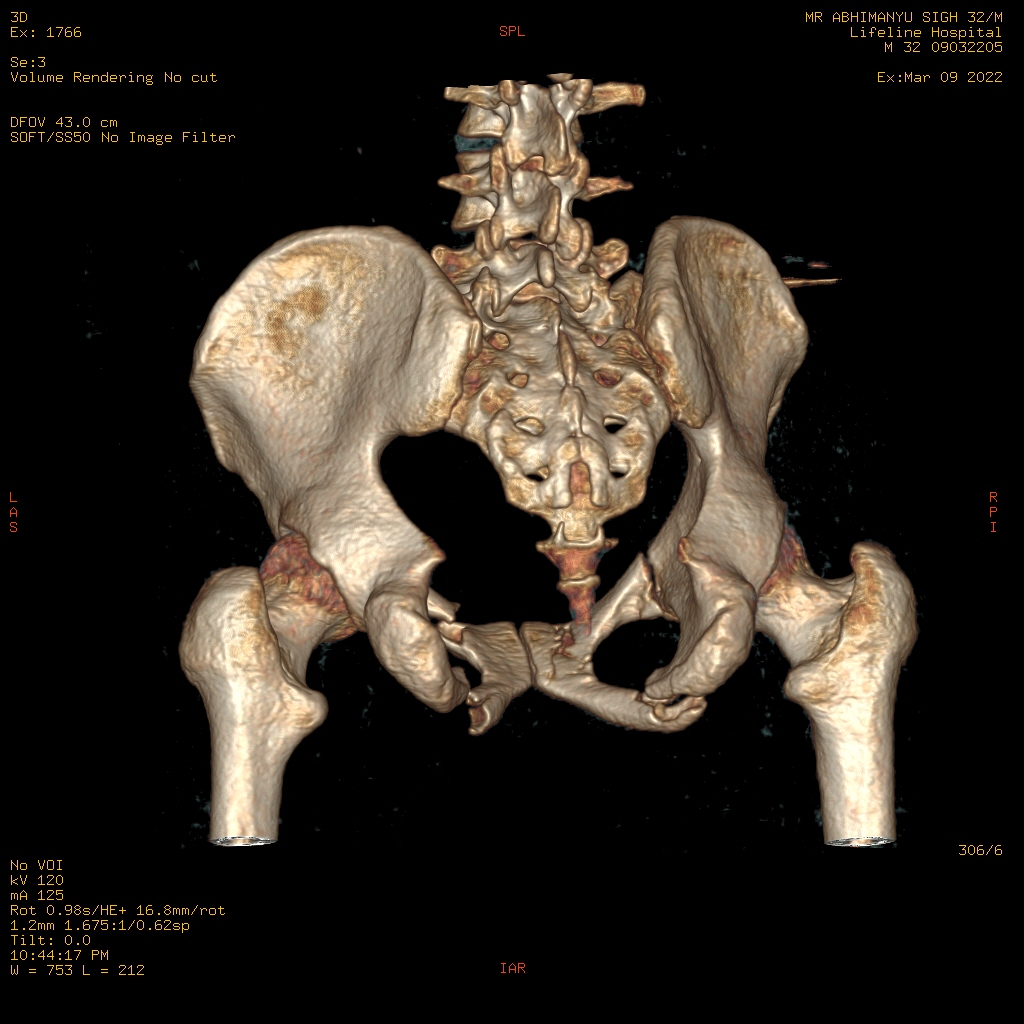 CT Scanner machines are differentiated by the number of slices they have, and the slice number correlates to how many images the CT scanning machine can garner per gantry rotation. For example, a 32 Slice CT Scan machine is capable of acquiring 32 images per gantry rotation.
CT Scanner machines are differentiated by the number of slices they have, and the slice number correlates to how many images the CT scanning machine can garner per gantry rotation. For example, a 32 Slice CT Scan machine is capable of acquiring 32 images per gantry rotation.
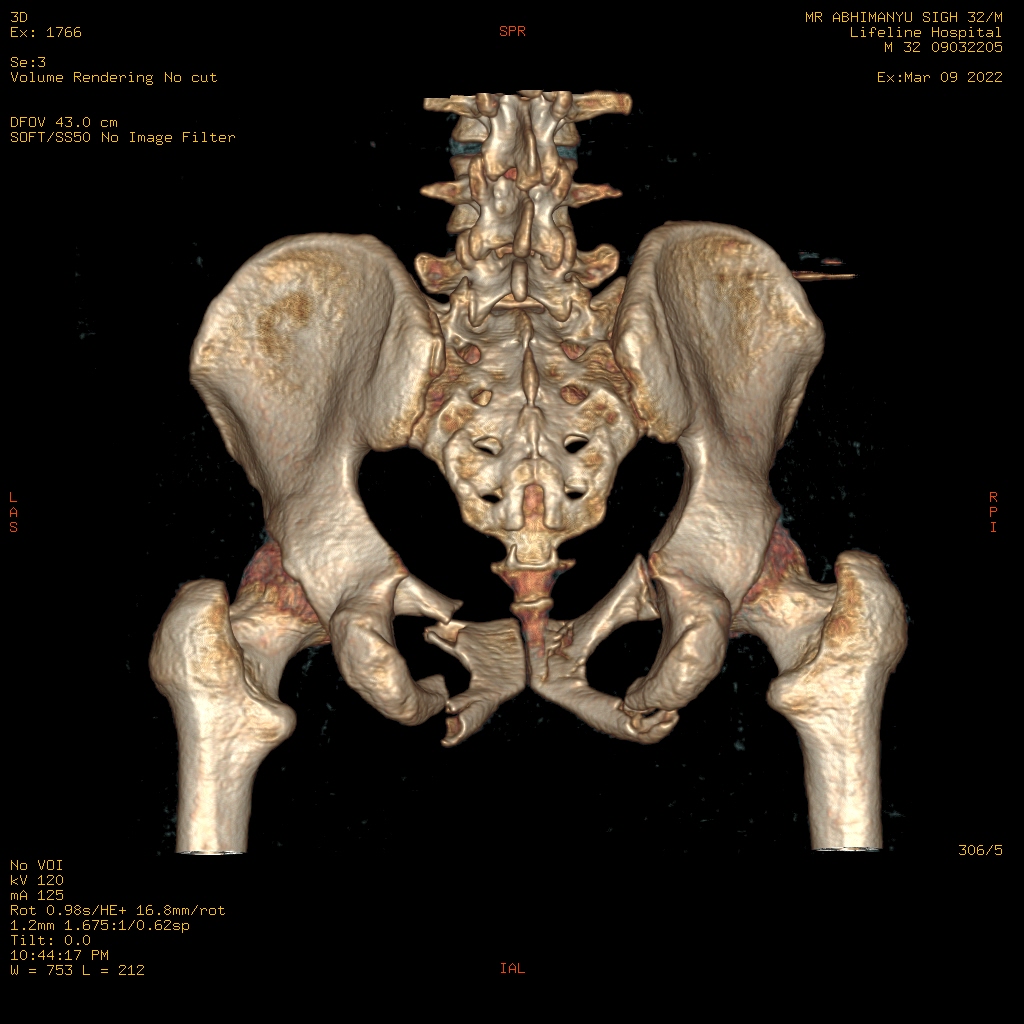
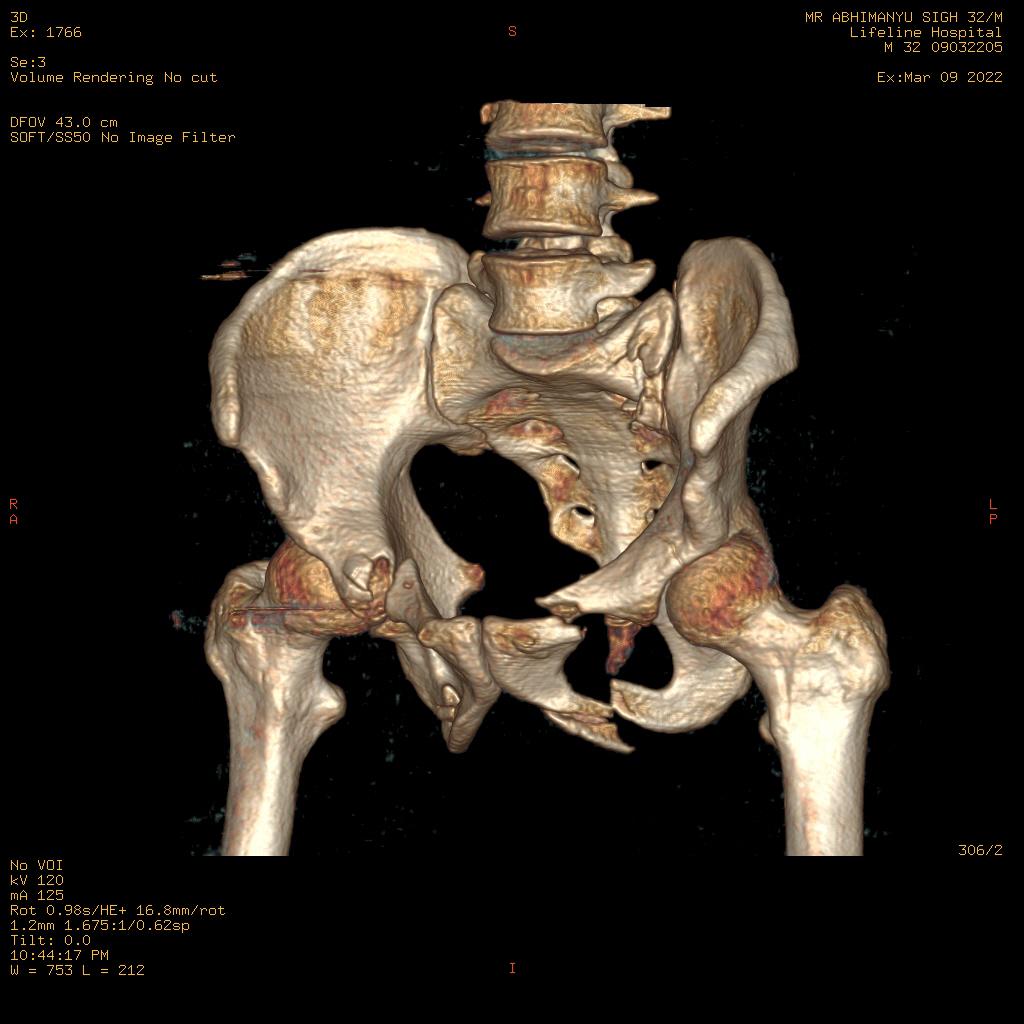
 CT Scanner machines are differentiated by the number of slices they have, and the slice number correlates to how many images the CT scanning machine can garner per gantry rotation. For example, a 32 Slice CT Scan machine is capable of acquiring 32 images per gantry rotation.
CT Scanner machines are differentiated by the number of slices they have, and the slice number correlates to how many images the CT scanning machine can garner per gantry rotation. For example, a 32 Slice CT Scan machine is capable of acquiring 32 images per gantry rotation.
CT has become an important tool in medical imaging to supplement X-rays and medical ultrasonography. It has more recently been used for preventive medicine or screening for disease, for example CT colonography for people with a high risk of colon cancer, or full-motion heart scans for people with high risk of heart disease.

Head
 CT scanning of the head is typically used to detect infarction, tumors, calcifications, haemorrhage, and bone trauma. Of the above, hypodense (dark) structures can indicate edema and infarction, hyperdense (bright) structures indicate calcifications and haemorrhage and bone trauma can be seen as disjunction in bone windows. Tumors can be detected by the swelling and anatomical distortion they cause, or by surrounding edema. Ambulances equipped with small bore multi-slice CT scanners respond to cases involving stroke or head trauma. CT scanning of the head is also used in CT-guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of intracranial tumors, arteriovenous malformations, and other surgically treatable conditions using a device known as the N-localizer
CT scanning of the head is typically used to detect infarction, tumors, calcifications, haemorrhage, and bone trauma. Of the above, hypodense (dark) structures can indicate edema and infarction, hyperdense (bright) structures indicate calcifications and haemorrhage and bone trauma can be seen as disjunction in bone windows. Tumors can be detected by the swelling and anatomical distortion they cause, or by surrounding edema. Ambulances equipped with small bore multi-slice CT scanners respond to cases involving stroke or head trauma. CT scanning of the head is also used in CT-guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of intracranial tumors, arteriovenous malformations, and other surgically treatable conditions using a device known as the N-localizer
Neck
Contrast CT is generally the initial study of choice for neck masses in adults. CT of the thyroid plays an important role in the evaluation of thyroid cancer.Also, CT scans often incidentally find thyroid abnormalities, and thereby practically becomes the first investigation modality.
Lungs
A CT scan can be used for detecting both acute and chronic changes in the lung parenchyma, the tissue of the lungs. It is particularly relevant here because normal two-dimensional X-rays do not show such defects. A variety of techniques are used, depending on the suspected abnormality. For evaluation of chronic interstitial processes such as emphysema, and fibrosis, thin sections with high spatial frequency reconstructions are used; often scans are performed both on inspiration and expiration. This special technique is called high resolution CT that produces a sampling of the lung, and not continuous images.
Angiography
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is contrast CT to visualize the arteries and veins throughout the body. This ranges from arteries serving the brain to those bringing blood to the lungs, kidneys, arms and legs. An example of this type of exam is CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) used to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It employs computed tomography and an iodine-based contrast agent to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries.
 Ultrasound imaging is an effective method of diagnosing unexplained pain, swelling and infection. It can provide imaging guidance for needle biopsies or evaluate conditions related to blood flow. Ultrasound is also the preferred imaging method for monitoring a pregnant woman and her unborn child.
Ultrasound imaging is an effective method of diagnosing unexplained pain, swelling and infection. It can provide imaging guidance for needle biopsies or evaluate conditions related to blood flow. Ultrasound is also the preferred imaging method for monitoring a pregnant woman and her unborn child.
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is used to help diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body's internal organs and to examine a baby in pregnant women and the brain and hips in infants. It's also used to help guide biopsies, diagnose heart conditions, and assess damage after a heart attack. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation.
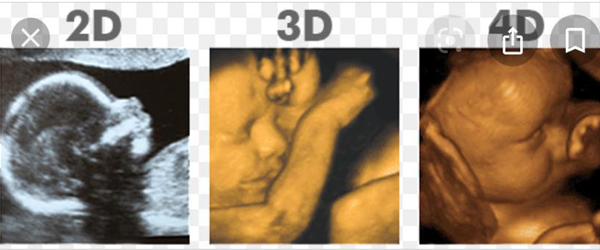 An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to make an image of a person's internal body structures. Doctors commonly use ultrasound to study a developing fetus (unborn baby), a person's abdominal and pelvic organs, muscles and tendons, or their heart and blood vessels.
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to make an image of a person's internal body structures. Doctors commonly use ultrasound to study a developing fetus (unborn baby), a person's abdominal and pelvic organs, muscles and tendons, or their heart and blood vessels.
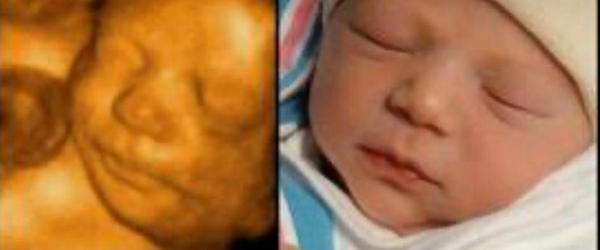 The ultrasound image is produced based on the reflection of the waves off of the body structures. The strength (amplitude) of the sound signal and the time it takes for the wave to travel through the body provide the information necessary to produce an image.
The ultrasound image is produced based on the reflection of the waves off of the body structures. The strength (amplitude) of the sound signal and the time it takes for the wave to travel through the body provide the information necessary to produce an image.
Mammography breast imaging uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early —when it is most treatable. Mammography plays a leading role in early detection, because it can show changes in the breast up to two years before you or your physician can feel them.
To evaluate the health of specific areas of the body, one or more radiology techniques are often used in combination. Radiology can accurately screen for: